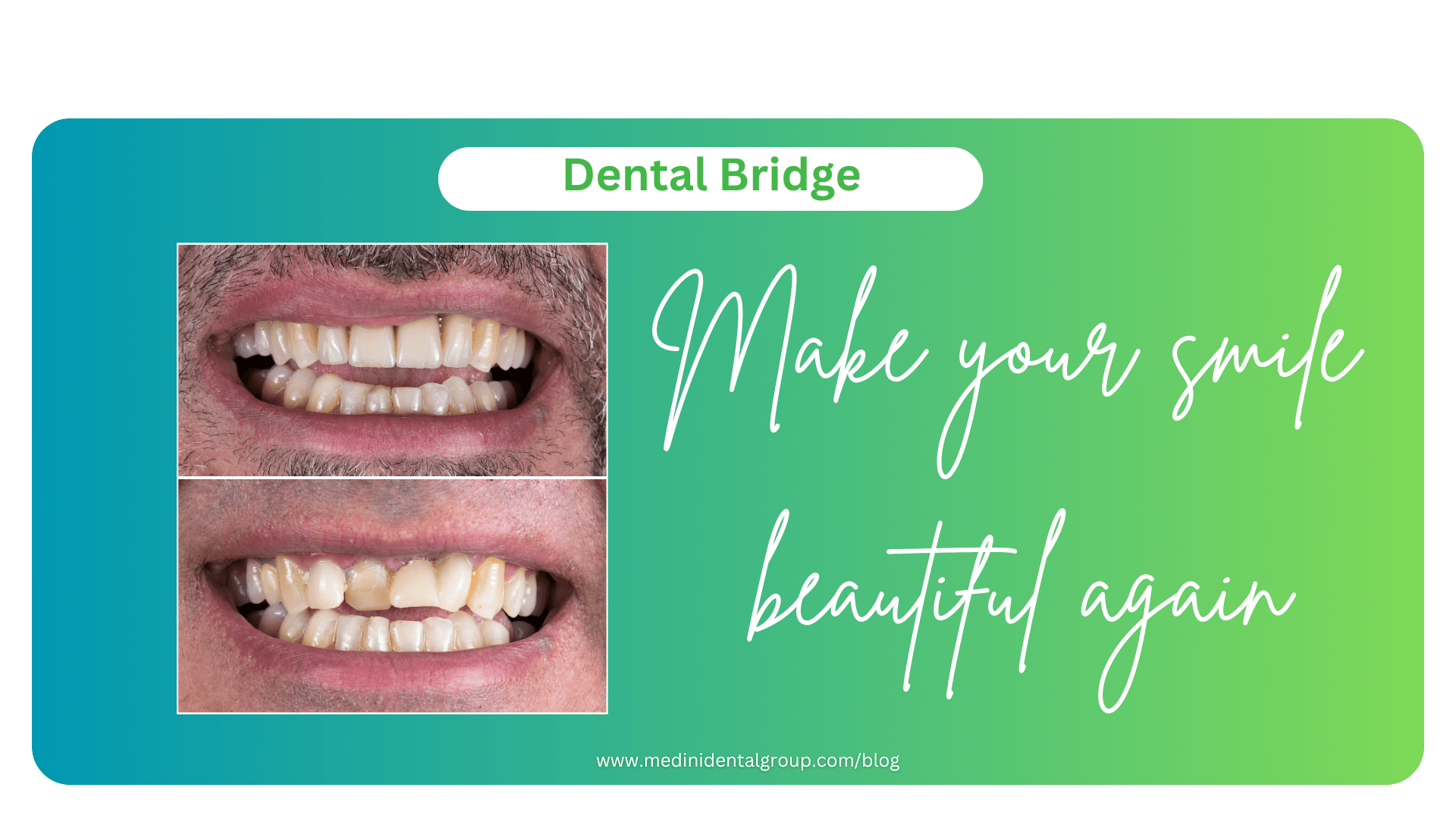
Dental Bridges: Price, Procedure & Risks – Everything You Need to Know
When tooth loss occurs, dental bridges offer a highly effective and aesthetically pleasing solution. Whether caused by decay, injury, or age, missing teeth can lead to a cascade of oral health problems. Dental bridges not only restore your smile but also maintain proper bite alignment and prevent adjacent teeth from shifting. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the cost, types, step-by-step procedure, risks, and aftercare of dental bridges to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Dental Bridge?
A dental bridge is a prosthetic device that “bridges” the gap created by one or more missing teeth. It consists of two or more crowns placed on either side of the gap—called abutment teeth—with a false tooth or teeth (pontics) in between. These artificial teeth can be made from porcelain, alloys, gold, or a combination of these materials.
Types of Dental Bridges
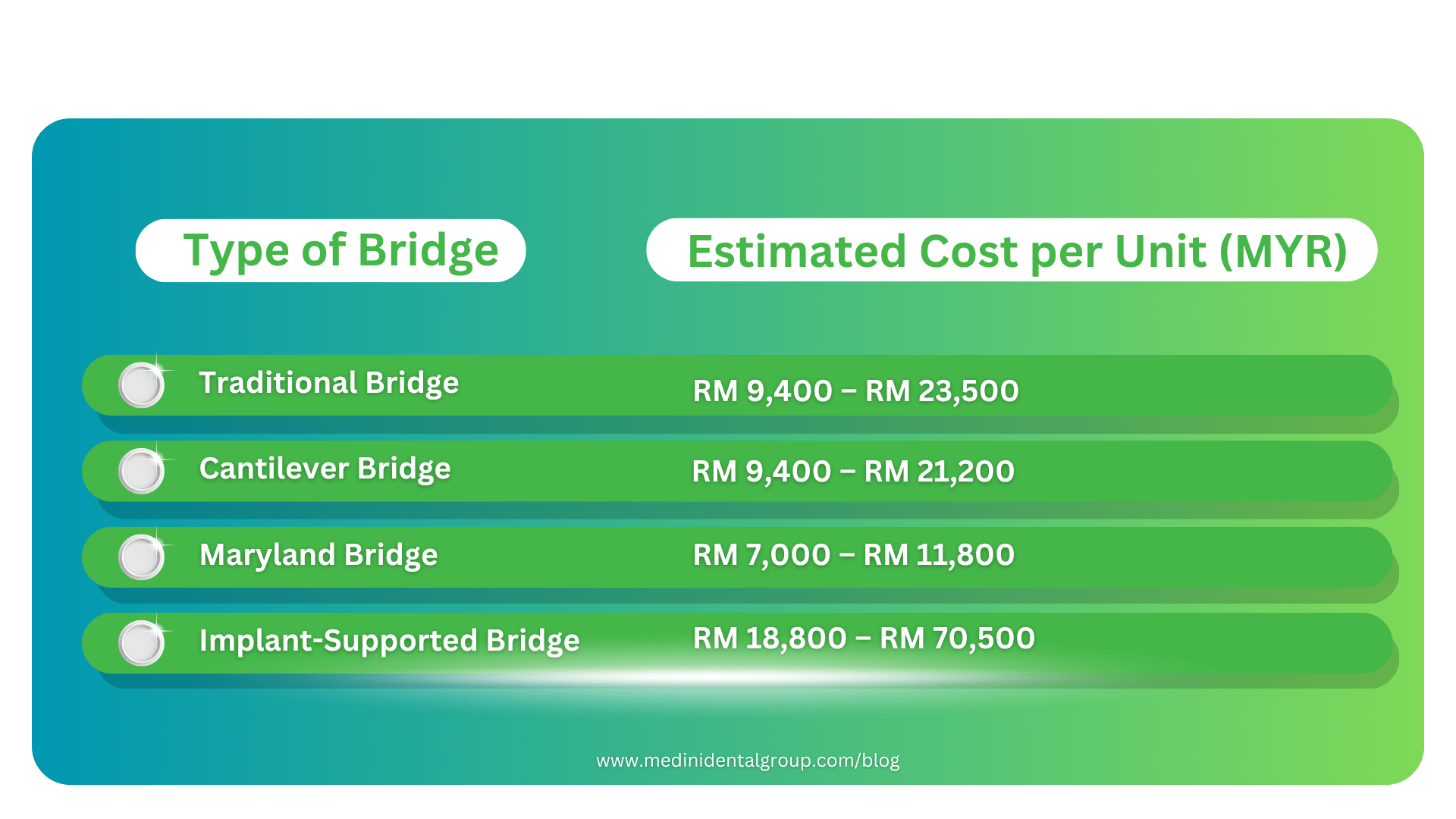
1. Traditional Dental Bridge
The most common type, a traditional bridge, involves creating crowns for the teeth on either side of the missing tooth, with a pontic in between. This type is ideal when you have natural teeth on both sides of the gap.
2. Cantilever Bridge
Used when there are natural teeth only on one side of the missing tooth. Less common and not suitable for areas under heavy bite pressure, such as molars.
3. Maryland Bonded Bridge
Also known as a resin-bonded bridge, it involves a metal or porcelain framework bonded to the backs of the adjacent teeth. It’s minimally invasive but less durable than other types.
4. Implant-Supported Bridge
This is the most stable and long-lasting option. It uses dental implants instead of natural teeth for support and is ideal for patients missing several teeth in a row.
Cost of Dental Bridges
The price of a dental bridge depends on several factors:
-
Type of bridge used
-
Material (porcelain, zirconia, gold, etc.)
-
Location of the dental clinic
-
Experience of the dentist
-
Number of missing teeth
Here’s a breakdown of the estimated cost:
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Initial Consultation
During your first visit, your dentist will perform a comprehensive oral examination, take X-rays, and discuss the most suitable type of bridge for your condition.
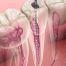
2. Tooth Preparation
The abutment teeth are reshaped to accommodate the crowns. This involves removing a portion of enamel under local anesthesia to ensure a proper fit for the bridge.
3. Impressions
Your dentist will take digital or physical impressions of your teeth to fabricate the custom bridge in a dental lab. Temporary bridges may be placed in the meantime.
4. Bridge Placement
Once the bridge is ready (usually in 1–2 weeks), the temporary bridge is removed, and the permanent one is cemented or attached into place. The dentist ensures proper bite alignment and makes any necessary adjustments.
5. Follow-Up
A follow-up visit is typically scheduled within a week to ensure everything fits well and functions as intended.
Risks and Complications
While dental bridges are considered safe and effective, there are potential risks and side effects:
-
Tooth sensitivity: Common in the initial days post-procedure.
-
Decay under crowns: If proper oral hygiene is not maintained.
-
Bridge failure: Often due to weak abutment teeth or improper fitting.
-
Gum disease: Can compromise the stability of the bridge.
-
Loosening of the bridge: Especially in Maryland or cantilever bridges.
Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene can significantly reduce these risks.
Benefits of Dental Bridges
-
Restored smile and facial shape
-
Improved chewing and speaking ability
-
Even distribution of bite force
-
Prevention of teeth shifting
-
Durability with proper care (lasting 5–15 years)
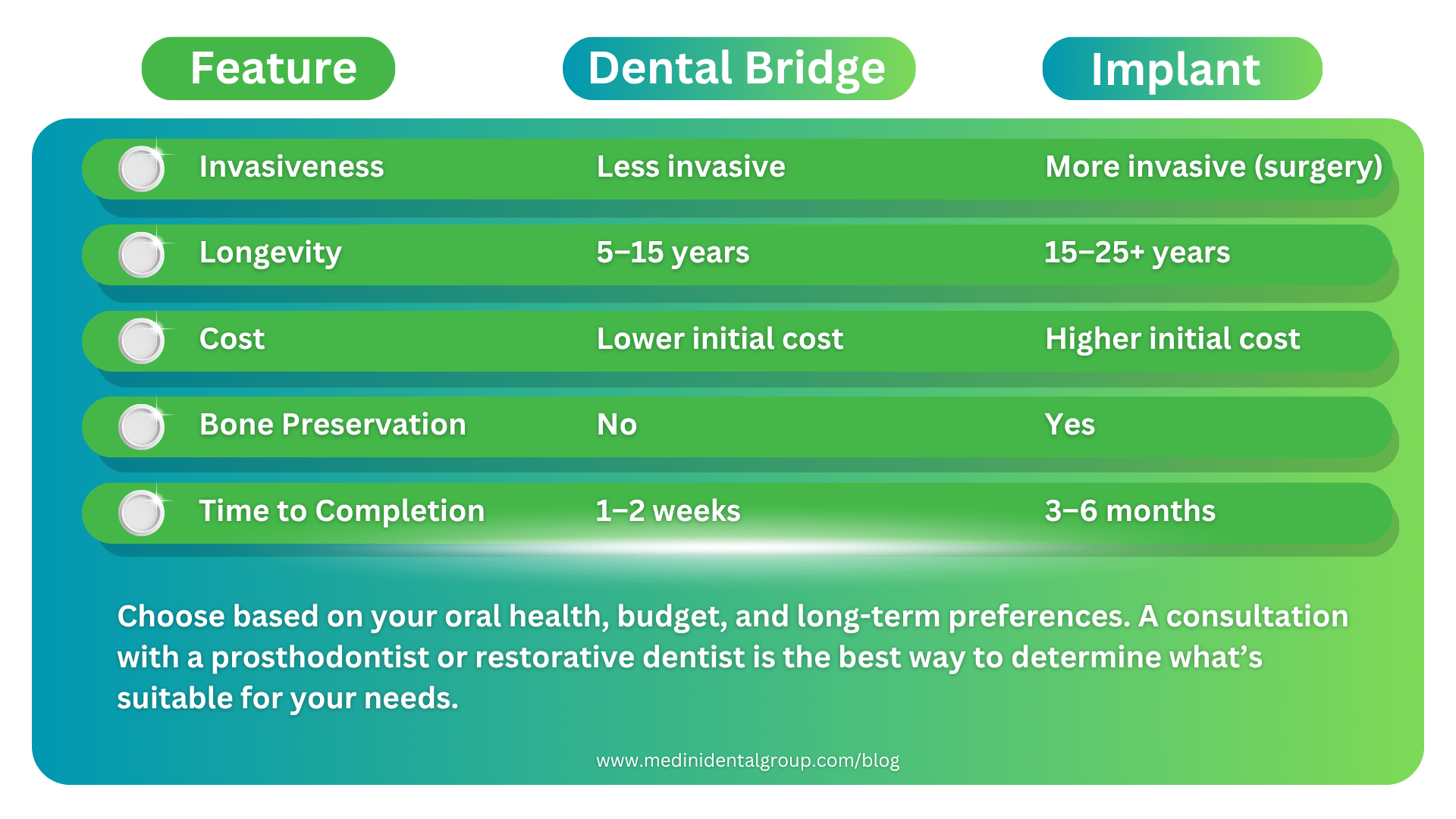
Dental Bridge vs. Implant – Which is Better?
How to Care for Your Dental Bridge
Proper care ensures longevity and oral health. Here are key tips:
-
Brush twice daily using a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
-
Floss daily using a floss threader or special dental bridge floss.
-
Use an antibacterial mouthwash to prevent plaque buildup.
-
Avoid hard foods like ice, nuts, and sticky candy.
-
Visit your dentist every 6 months for routine check-ups and cleanings.
Who is a Candidate for a Dental Bridge?
You may be an ideal candidate if:
-
You have one or more missing teeth.
-
You have healthy teeth or implants to support the bridge.
-
You’re committed to oral hygiene and regular dental visits.
-
You do not have advanced periodontal disease or jawbone loss.
How Long Do Dental Bridges Last?
With proper care, dental bridges typically last:
-
5 to 7 years on average.
-
10 to 15 years with exceptional care and no complications.
Factors like oral hygiene, diet, grinding habits, and dental health conditions influence longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is getting a dental bridge painful?
The procedure is usually painless due to local anesthesia. You may experience mild discomfort or sensitivity afterward, which subsides in a few days.
2. Can I eat normally with a dental bridge?
Yes, once the bridge settles, you can eat most foods. It’s best to avoid extremely hard or sticky items to prevent damage.
3. Will a dental bridge affect my speech?
Initially, some patients notice slight changes, but normal speech returns quickly as you adapt.
4. Can a bridge be repaired if it breaks?
Minor damage may be repairable. However, significant issues often require replacing the entire bridge.
Conclusion
Dental bridges offer a cost-effective, durable, and aesthetically pleasing solution for missing teeth. Whether you choose a traditional, implant-supported, or resin-bonded option, a dental bridge can restore not only your smile but also your confidence and oral health. By understanding the pricing, procedure, and risks, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your dental goals.